Introduction
VPS hosting explained in simple terms: it is a type of web hosting that provides dedicated resources within a virtual server environment.This VPS hosting explained guide helps website owners understand when upgrading from shared hosting makes sense.
As your website grows, shared hosting often becomes limiting. Slow loading speeds, performance drops during traffic spikes, and restricted control can hold your business back.VPS hosting is one of the most popular options explained in our complete Web Hosting Explained: Beginner to Advanced Guide (2026).
That’s where VPS hosting comes in.
In this guide, we’ll explain:
- What VPS hosting is
- How it works
- Its advantages and disadvantages
- Who should use it
- When to upgrade from shared hosting
Whether you’re running a business site, eCommerce store, or growing blog, this guide will help you decide if VPS hosting is right for you.If you’re comparing options, read our detailed breakdown of different types of web hosting to understand where VPS fits.
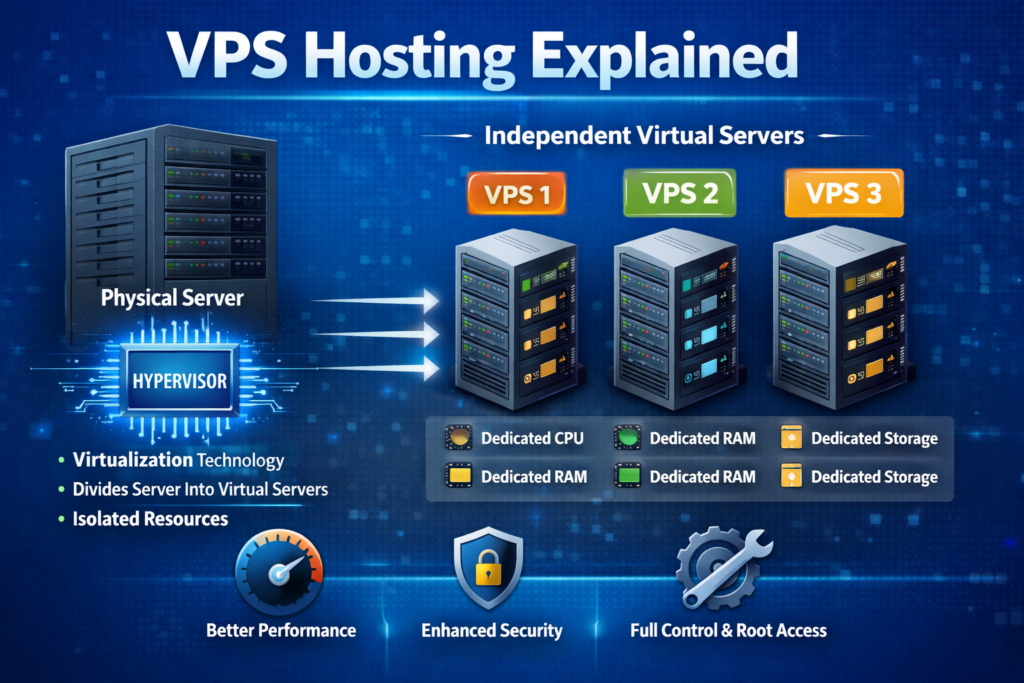
What Is VPS Hosting?(VPS Hosting Explained Simply)
VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting is a type of web hosting where a physical server is divided into multiple virtual servers using virtualization technology.
Each VPS acts like an independent server with:
- Dedicated CPU allocation
- Dedicated RAM
- Dedicated storage
- Its own operating system
Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared among hundreds of users, VPS gives you isolated resources.
Think of it like this:
- Shared hosting = Renting a room in a house
- VPS hosting = Renting your own apartment
- Dedicated server = Owning the entire building
How Does VPS Hosting Work?
VPS hosting works using virtualization technology, where a hypervisor divides a physical server into multiple isolated virtual machines. This concept is explained in detail on Wikipedia’s page about virtualization.
Each virtual server:
- Operates independently
- Can be rebooted individually
- Has root access (in most plans)
- Runs its own OS (Linux or Windows)
Even though multiple VPS accounts exist on the same physical machine, they do not interfere with each other like shared hosting accounts can.
This isolation is what improves performance and stability.
VPS Hosting vs Shared Hosting
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting |
| Resources | Shared with others | Dedicated allocation |
| Performance | Can fluctuate | Stable & predictable |
| Control | Limited | Full root access |
| Security | Basic isolation | Strong isolation |
| Price | Low | Moderate |
| Best For | Beginners | Growing websites |
If you haven’t read it yet, check our detailed breakdown of shared hosting to understand the difference better.
Types of VPS Hosting
There are two main types:
Managed VPS
Hosting provider handles:
- Server setup
- Security Updates
- Monitoring
- Technical maintenance
Best for:
- Business owners
- Non-technical users
- Agencies
Unmanaged VPS
You are responsible for:
- Server configuration
- Software installation
- Security setup
- Maintenance
Best for:
- Developers
- Sysadmins
- Advanced users
Unmanaged VPS is cheaper but requires technical skills.
Benefits of VPS Hosting
Better Performance
Since resources are allocated specifically to you, your website won’t slow down due to other users’ traffic spikes.
Improved Security
Your VPS environment is isolated. Other users on the server cannot access your files.
Scalability
Need more RAM or CPU? VPS plans can often be upgraded without migrating servers.
Full Root Access
Install custom applications, configure firewalls, optimize performance — full control.
Cost-Effective Upgrade
It offers near-dedicated performance at a fraction of the cost.
Drawbacks of VPS Hosting
❌ Higher Cost Than Shared Hosting
VPS costs more because resources are dedicated.
❌ Requires Technical Knowledge
Especially unmanaged plans.
❌ Server Responsibility
Security and updates are critical if unmanaged.
Who Should Use VPS Hosting?
VPS hosting is ideal for:
- Growing business websites
- eCommerce stores
- High-traffic blogs
- Web applications
- Agencies hosting multiple client sites
- Users needing custom server configuration
If your website receives more than 20,000–30,000 monthly visitors, VPS is usually the next logical step.
When Should You Upgrade to VPS?
You should consider upgrading if:
- Your website loads slowly
- You frequently hit resource limits
- You need custom software installation
- Traffic is increasing
- Your hosting provider recommends upgrade
If you’re seeing CPU limit warnings in cPanel, it’s often time to move to VPS.If you’re currently on shared hosting, upgrading to VPS can improve performance significantly.
VPS Hosting vs Cloud Hosting
Many people confuse VPS and cloud hosting.
VPS Hosting
- Runs on one physical server
- Predictable resources
- Cost stable
Cloud Hosting
- Uses multiple interconnected servers
- High scalability
- Often pay-as-you-go
Cloud is better for very large or unpredictable traffic spikes.
Is VPS Hosting Worth It in 2026?
Yes — especially for:
- Business websites
- SaaS projects
- Content-heavy platforms
- Websites generating revenue
Frequently Asked Questions
Is VPS hosting faster than shared hosting?
Yes. Because resources are dedicated, performance is significantly more stable.
Do I need technical skills for VPS?
Only for unmanaged VPS. Managed VPS removes most technical complexity.
Can I upgrade from shared hosting to VPS easily?
Most hosting providers offer seamless upgrades.
Is VPS good for WordPress?
Yes, especially for high-traffic WordPress websites.
In this VPS hosting explained article, we covered how it works, its benefits, and when to upgrade.
Final Thoughts
VPS hosting is the natural upgrade path when shared hosting becomes limiting.
It offers:
- Better performance
- More control
- Higher security
- Scalability
If you’re serious about growing your website, VPS hosting is often the smartest next step.Businesses that need privacy-focused infrastructure often choose offshore VPS hosting solutions for added flexibility.